Introduction
Arrays are something that we can't ignore, one must have heard about this term before. And I am pretty sure that you must be thinking about list of data, or collection of same elements stored collectively in a contagious memory that can be accessed by an index, and you are right to some extent but there is something more about arrays that you must know and, in this article, I'm going to break down every single concept about arrays and will make it as a piece of cake for you. And all I want is your precious time to read this article
What is an array?
An array is basically a collection or a list of similar items stored in a contagious memory location using a single variable name, where each item can be accessed by an index number. like storing all the student names in a class according to their roll numbers. Or storing the number of items required for cooking a dish. In simple words we can consider an array as a list of items indexed by numbers. In JavaScript arrays are not primitive type instead they are of object type i.e. arrays are not immutable. Arrays can be single or multidimensional. Single dimensional are basically what we call a list and multi-dimensional arrays are basically what we call matrices who's each element can be accessed by their index number, just like an excel sheet where box can be accessed by row and column number.
Defining an array & accessing the its elements
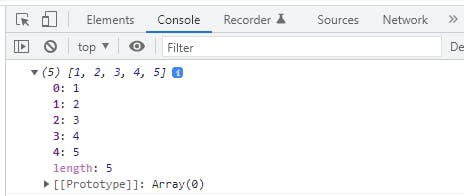
In JavaScript we can define an array using let or var keyword and putting the element in within third brackets [ ]
//defining a single dimensional array in JavaScript
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(array)
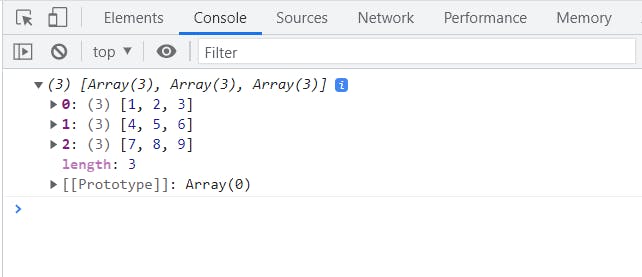
//define a 2d array
var arr = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
];
console.log(arr);
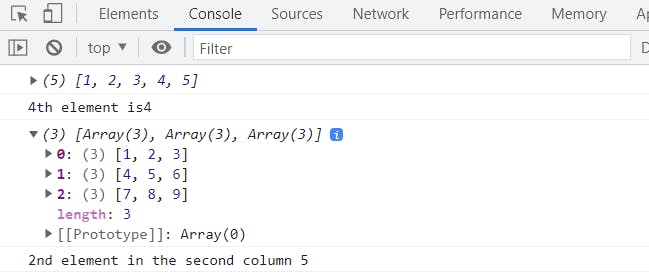
As I have mentioned earlier that every element in an array has an index number though which we can access it. In JavaScript we can access any element of an array using the syntax arrayname [indexnumber ]. One important note , an array index always starts from zero so if you want to access the 2nd element of an 1d array you have to use the 1 in place of index number
//define 1d array
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(array);
//syntax arrayname[index]
console.log("4th element is" + array[3]);
//define a 2d array
var arr = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
];
console.log(arr);
//syntax arrayname[row][col]
console.log("2nd element in the second column " + arr[1][1]);
Array methods simplified
A method is basically a predefined block code or a function that performs a particular task. In JavaScript , we have a set of predefined methods that we can use in arrays
length
This is not a method but a property which determines the length of an array
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.length);
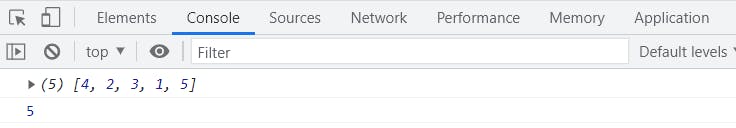 see this is giving us the length or the number of elements that our array contains
see this is giving us the length or the number of elements that our array contains
toString()
this method converts the array elements to a string
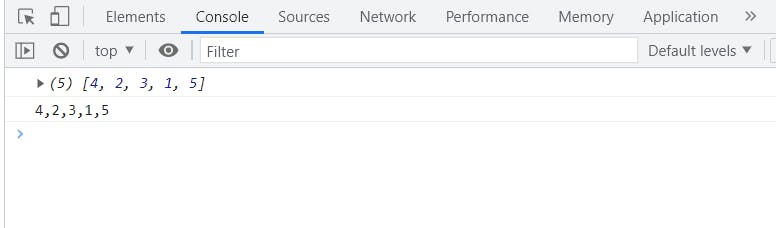
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.toString());
join()
this method also works like the toString() but you can add an operator to make your string look a bit different
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.join(" "));
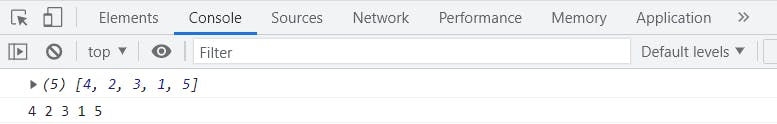
I am passing here space (" ") so our elements are separated by space
push(element)
If you want to dynamically add an element to an array you can use this method
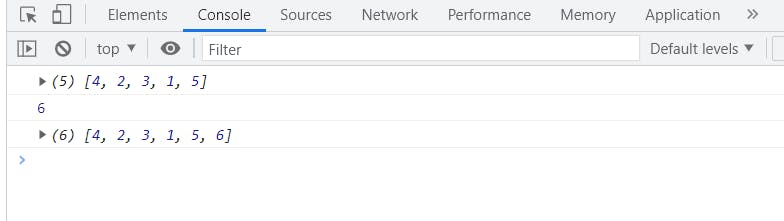
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.push(6));
console.log(array);
pop()
This method is used to remove the last element from an array
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.pop());
console.log(array);
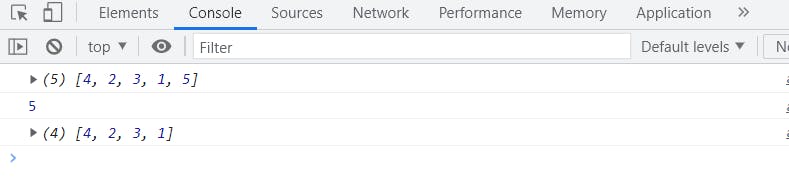
See 5 is popped out from our array
shift()
this method is used to remove the first element of an array
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.shift());
console.log(array);
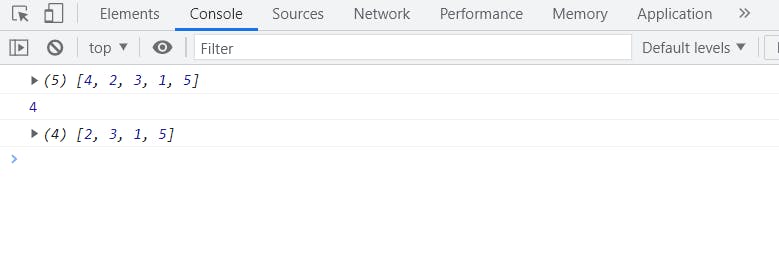 See
See 4 is shifted from our array
unshift()
This method is used to add an element in the beginning
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.unshift(7));
console.log(array);
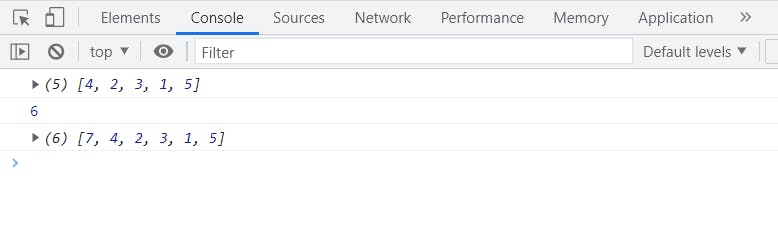
one thing you can notice here is that unshift() adds 7 in the beginning of our array in the other hand it returns the length of the new array
concat()
This method joins two arrays and return's a new one
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
let newarr = [3, 2, 1, 4, 5];
console.log(array);
console.log(newarr);
console.log(array.concat(newarr));
console.log(array);
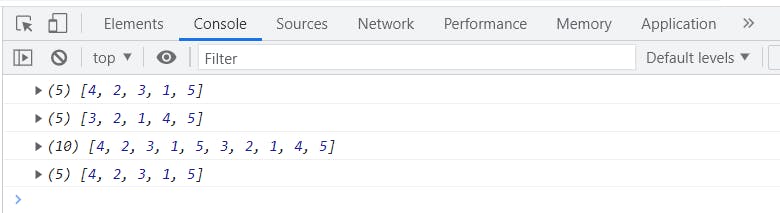
See this returns a new array of length 10
splice()
This method adds new items to an array at a particular position and can also remove elements
let array = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.splice(2, 1, 'a', 'b'));
console.log(array);
look at the code the splice method contains a pw parameters splice(startnumber,itemstobedeleted, items to be added)
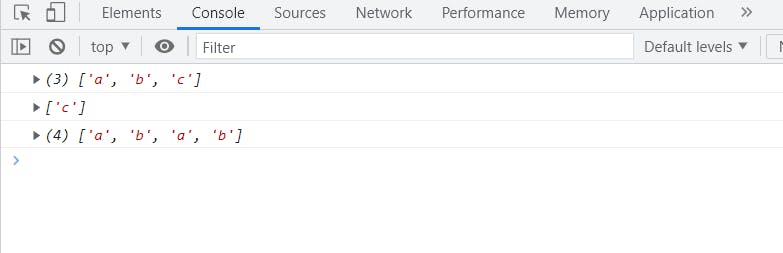
here in our example it is removing 1 element i.e. c from the 2 index and adding a,b there
slice()
this method removes a part from an array and returns a new one without affecting the original one
let array = ['a', 'b', 'c','e','f','g'];
console.log(array);
console.log(array.slice(2, 4));
console.log(array);
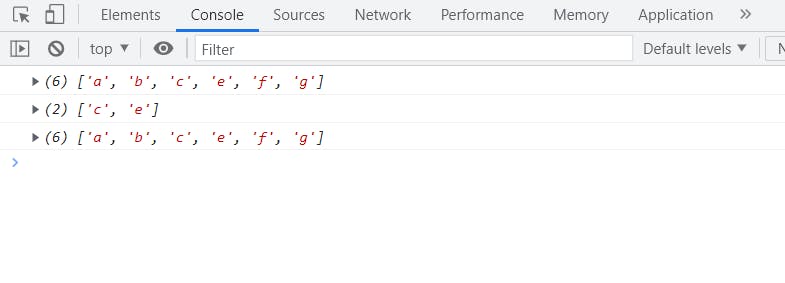
Iteration in an array
Iteration means repeating, now suppose you want to access a few elements of an array in an ordered way or simply you want to iterate over an array, and there are several ways to do so but I am going to show you the most used one's
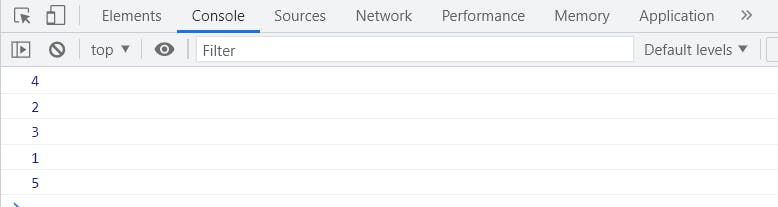
forEach()
It is used to iterate over the whole array from beginning to end
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
array.forEach(function (element) {
console.log(element);
});
map()
It basically creates a new array and performs a particular task within it
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
let result = array.map((item) => {
return item * 2;
});
console.log(result);
console.log(array);
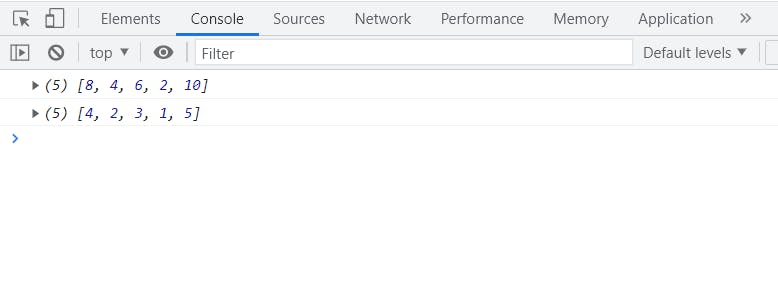
See a new array is created and the old array didn't change
filter()
This also creates a new array but only returns the values that pass a test or a condition
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
let result = array.filter((item) => {
return item > 3;
});
console.log(result);
console.log(array);
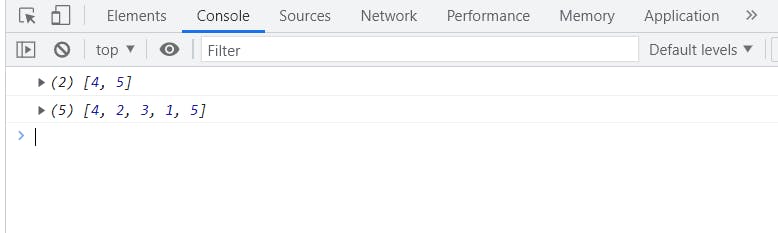 see this also creates a new array having values greater than
see this also creates a new array having values greater than 3
Sorting an array
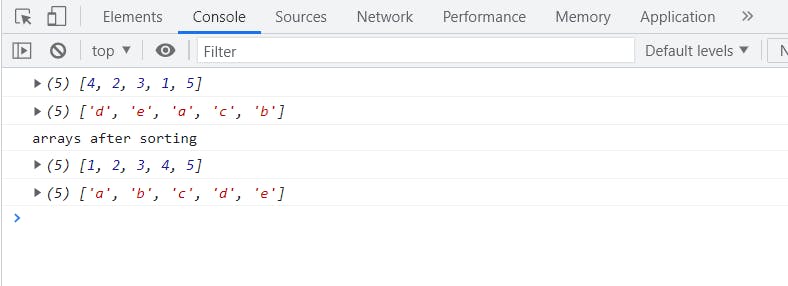
In JavaScript you can use the sort() method for sorting an array in alphabetical order for numeric arrays just pass a compare function within it as the sort function considers every array element as a String
let array = [4, 2, 3, 1, 5];
let strArray = ["d", "e", "a", "c", "b"];
console.log(array);
console.log(strArray);
console.log("arrays after sorting");
console.log(array.sort((a, b) => a - b));
console.log(strArray.sort());
Conclusion
So, guys this was all about arrays in JavaScript and the methods, feel free to comment if you have any queries, and do share this article with your friends and peers if you like it. Stay tuned for the next :)