
Common programming concepts you must know as a JavaScript Developer
Programming made easy
Intro
As of 2022 we can't imagine a world without computers , and a programming language is the only way to interact with our computers, like every application or features that we use in our daily life are basically a set of instructions that we have defined to a computer or a device using a programing language.
Suppose while using a calculator if you want to add two numbers (say 2 and 3 ) we use a + operator to get the result(5), which means that someone who made the calculator has defined that if a user uses the '+' operator the calculator will return them addition of inputs as a result via a language that it understands. In this article I am going to explain the most common concepts you will find in every programming language. And I am going to use JavaScript to explain all the concepts.
variables & Constants
Suppose if I ask you give me something to eat or give me some thing to drink then you will definitely serve me something to eat in a plate or say water to drink either in a bottle or a glass, i.e. I mean to say that the food and the water is contained by a container, similar in a programming language we store values in variables. like in mathematics you have often heard about the problem that if a=3 , b=5 what will be the value of (a+b) , here a , b are the variables which contains a value of 3, 5 respectively. constants are also same as variables the fact is that we cant change the value of a constant.
In JavaScript we define variables using var or let keyword and constants using const.
var radius = 3 //this is a global variable
const PI = 3.14 //this is a constant
/*Area of a circle*/
var area = PI * radius * radius
Identifiers & Keywords
Let me ask you a question , what is your name ? say John which means that you are a human and your identity is Jhon , Similarly I have a pet whose name is Scooby , so Scooby is the identifier of my name. In programming while defining variables we need an Identifier like var a = 5 here a is the identifier or if I say var hello =" I am a string ", here hello is the identifier . Keywords are basically the reserved words that you can't use as an identifiers . like const, if , else , var, let these are all keywords
Comments
Imagine you are working on a project which contains 1000 lines of code which contains 100's of variables and constants and functions, and then there it become difficult to find out which one is used for what . To avoid this type of situations programmers make notes within code like in the above example I have used comments to explain var and const . In JavaScript you can use //comment ere for single line comments and \*comment here *\ for multiple line comments. One more fact I would like to share that if often happens while debugging you can comment a few lines of code instead of deleting them and writing again .
// Hello I am a single line comment
var hello = "Hello World";
/* I am a multiline comment
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in
reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident,
sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.*/
/*I am commented code
var a = 5
*/
A print statement is basically a built in function which gives us the opportunity to display something on the screen like the result of sum of two numbers . In JavaScript we use document.write("output here ") or console.log("output here ") to display output. the former i used to discplay something on a html page and the later is used to display something in your browser's console
document.write("Helllo World");
console.log("Hello World");
var a = 5;
var b = 10;
console.log(a+b);
Inputs
In our daily life every single application or websites we use needs some inputs to show data needed by the user, consider you are searching something on Google or Bing and you need to enter something in the search bar so that Google or Bing can display results as per your needs. In JavaScript we use to prompt() take inputs from user or we can use a form if working with html.
prompt('Enter your name');
Datatypes
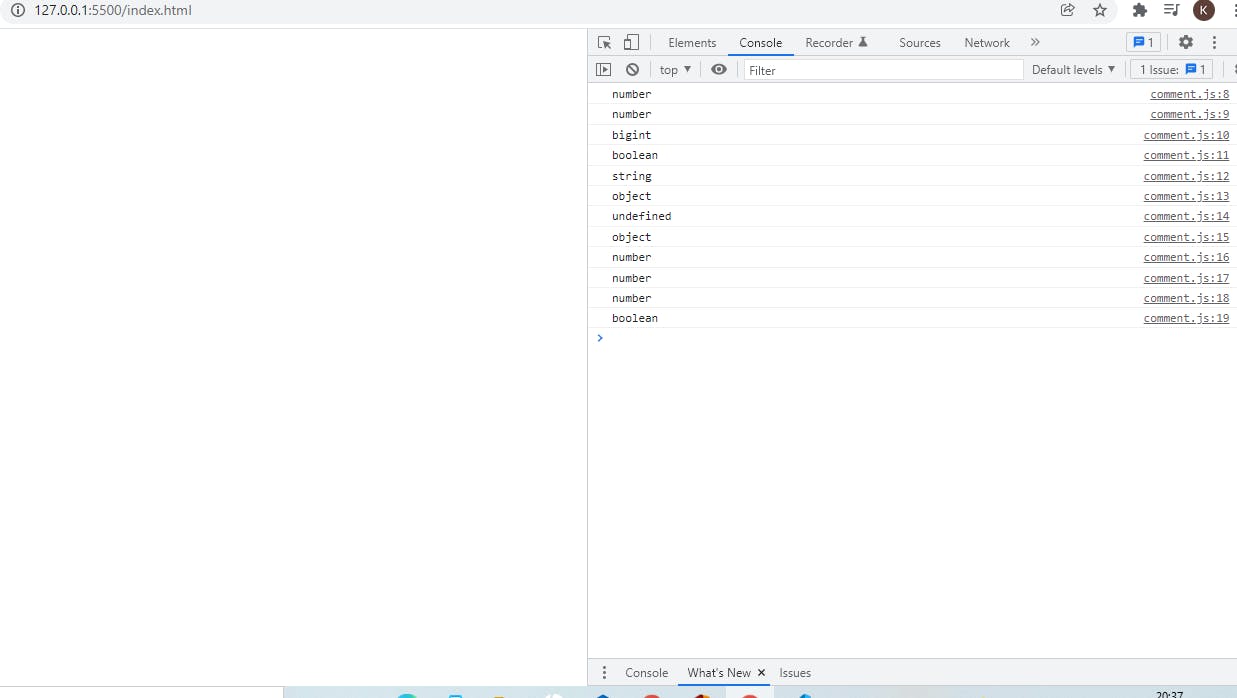
Remember those days when we were kids , we were taught about tastes like spicy, salty , sweet and bitter Similarly a programming language must know about which type of data it's dealing with, like the data can be a String or a Number or a Decimal or a Boolean , etc. Well in JavaScript we have two types of data viz, primitive type & Object type the former is immutable i.e it's value cant be changed and the later one is basically a value in the memory referred by an identifier.
var a = 5;
var b = 6.0000;
var d = 2n ** 53n;
var e = true;
var s = null;
var s = 'string';
var person = { name: "John", age: 34, isMarried: false };
console.log(typeof a);
console.log(typeof b);
console.log(typeof d);
console.log(typeof e);
console.log(typeof s);
console.log(typeof person);
console.log(typeof undefined);
console.log(typeof null);
console.log(typeof NaN);
console.log(typeof Infinity);
console.log(typeof -Infinity);
console.log(typeof true);
Arrays & Strings
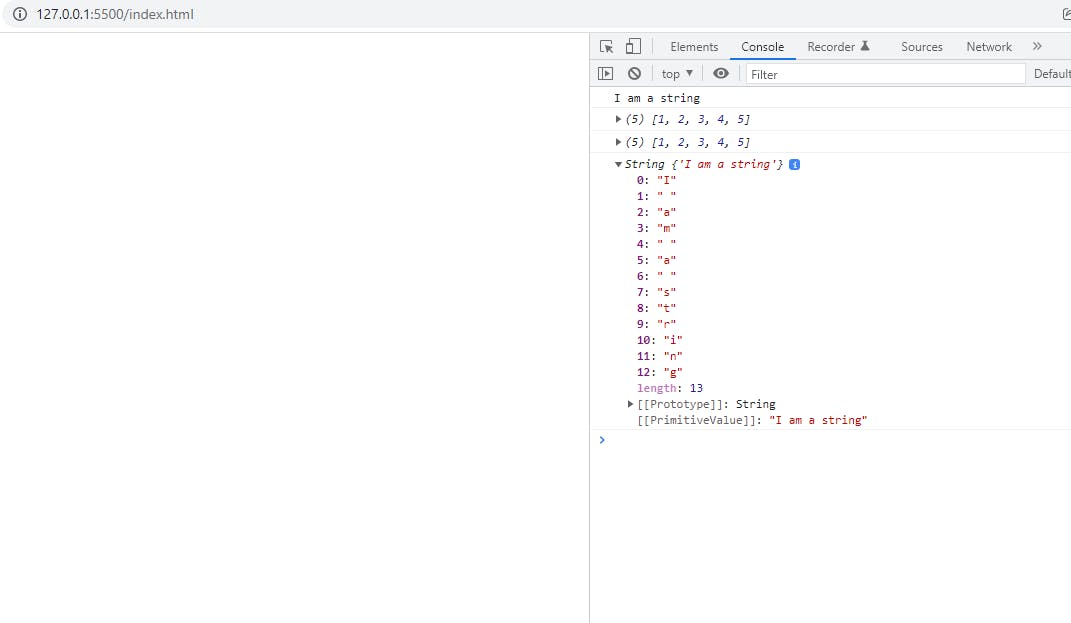
Consider a book shelf where we can store many books in one place similarly in programming we use an array to store a collection of similar type of data elements at a contagious memory location and a string is something which we can consider as an array of characters. In JavaScript we can define an array or a string using the var or let keyword
let hello = "I am a string";
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
/*using constructors*/
let arr2 = new Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
let str = new String("I am a string");
console.log(hello);
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr2);
console.log(str);
Conditionals
Imagine a situation, that you have given an exam and now there are two possibilities that either you pass or you fail now if you pass you get promoted to the next level and if you fail will have to complete the previous session again. In programming we also get some situations where we have to work with conditionals like while you login to your Instagram account it asks you to enter your userid and password and if you enter correct credentials on then it Gona redirect you to your profile or it will show you an error or it will advice you to change your password if you have forgotten and these things are happening because of conditionals. In JavaScript we have if , elseand elseif statements for applying conditionals .
var userid = prompt("Enter your userid");
var password = prompt("Enter your password");
if (userid == "admin" && password == "password") {
alert("Welcome Admin!");
}
else if (userid == "user" && password != "pass") {
alert("Welcome User!");
}
else {
alert("Wrong userid or password");
}
flow of control
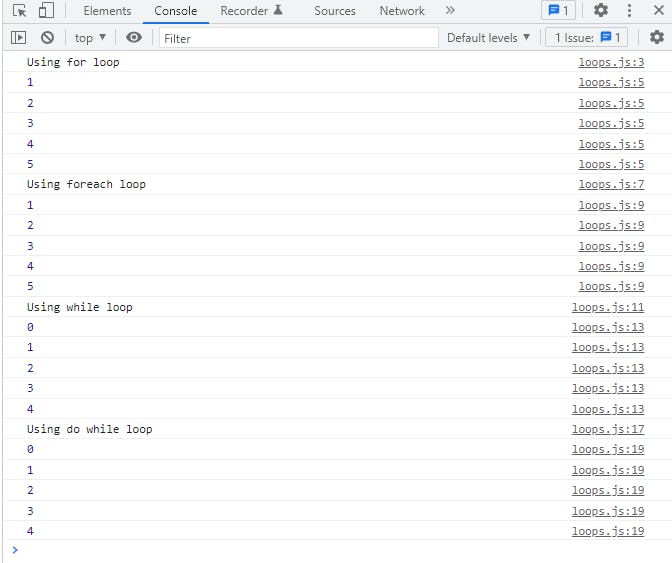
suppose you are given a homework of writing I am a good boy 100 times so what you are going to do you will start writing the sentence until you repeat it 100 times. i.e You are repeating a particular task until a condition is achieved. In programming also we often get some scenarios where e need to repeat a particular task until a condition is achieved and to do so we use flow of control statements or what we call loops in plain English . In JavaScript we have several flow of control statements
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var n = 0;
console.log("Using for loop");
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(arr[i]);
}
console.log("Using foreach loop");
arr.forEach(element => {
console.log(element);
})
console.log("Using while loop");
while (n < 5) {
console.log(n);
n = n + 1;
}
var k = 0
console.log("Using do while loop");
do {
console.log(k);
k = k + 1;
}
while (k < 5);
Operations
Now operators are basically symbols to perform an operation between two operands , like a +b here + is an operator . In JavaScript we have
- Arithmetic operators
to perform mathematical tasks like addition , division ,etc.
/*Arithmetic operators*/
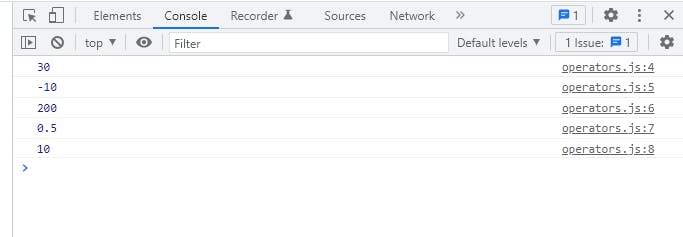
var a = 10;
var b = 20;
console.log(a + b);
console.log(a - b);
console.log(a * b);
console.log(a / b);
console.log(a % b);
- Assignment Operators
for assigning values
/*Assignment operators*/
var c = 10;
console.log(c += 10);
console.log(c -= 10);
console.log(c *= 10);

- Comparison Operators
for comparing two operands
/*Comparison operators*/
var d = 10;
var e = 20;
console.log(d > e);
console.log(d < e);
console.log(d >= e);
console.log(d <= e);

- Logical Operators
to make a logical decision
/*Logical operators*/
var x = true
var y = false
console.log(x && y);
console.log(x || y);
console.log(!x);

- Bitwise Operators
to perform bitwise operations
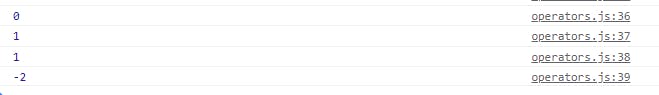
/*Bitwise operators*/
var p = true
var q = false
console.log(p & q);//and
console.log(p | q);//or
console.log(p ^ q);//xor
console.log(~p);//not
Functions
It often happens that we need to implement a particular task multiple times what I mean to say that in my last example I gave an example of user login , now Instagtram often asks to enter your password if you want to change any personal info , so instead of rewriting a same lines of code many times we can define a function and can use as needed , i.e. are basically reusing our code . In JavaScript we use a function keyword to define a function
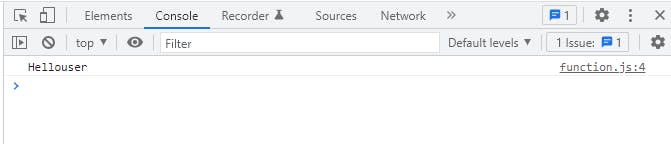
//defining a function
function sayHello(name) {
console.log("Hello" + name);
}
sayHello("user ")//calling a function
Outro
Kudos you have completed reading this article. This was all you need to know about the most common programming concepts .One thing I would like to highlight is that while reading this article run the code snippets in your browser to understand more clearly . Feel free to post a comment if you have any queries. And share this article with your peers and collogues if you find this helpful. Stay Happy and Safe .